Selective Inhibition of Human Type-5 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase (AKR1C3) by Baccharin, a Component of Brazilian Propolis
The human aldo-keto reductase (AKR) 1C3, also known as type-5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and prostaglandin F synthase, has been suggested as a therapeutic target in the treatment of prostate and breast cancers.
In this study, AKR1C3 inhibition was examined by Brazilian propolis-derived cinnamic acid derivatives that show potential antitumor activity, and it was found that baccharin (1) is a potent competitive inhibitor (K(i) 56 nM) with high selectivity, showing no significant inhibition toward other AKR1C isoforms (AKR1C1, AKR1C2, and AKR1C4).
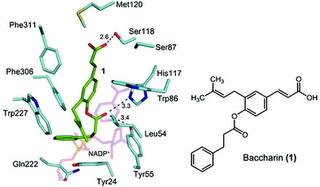
Molecular docking and site-directed mutagenesis studies suggested that the nonconserved residues Ser118, Met120, and Phe311 in AKR1C3 are important for determining the inhibitory potency and selectivity of 1. The AKR1C3-mediated metabolism of 17-ketosteroid and farnesal in cancer cells was inhibited by 1, which was effective from 0.2 μM with an IC(50) value of about 30 μM. Additionally, 1 suppressed the proliferation of PC3 prostatic cancer cells stimulated by AKR1C3 overexpression.
This study is the first demonstration that 1 is a highly selective inhibitor of AKR1C3.